Post by Iqbal Zulkarnain on Jul 23, 2012 15:38:16 GMT 7
[glow=red,2,300]ABC For Decision Making[/glow]
ABC ? sounds like soy souce brand ;D
What is ABC ? Lets continue read…..
Today, Internet is a rapidly growing market for multimedia services delivered to mobile devices, so called mobile internet Mobile. Mobile internet growth explosive on recent year. Mobile data traffic going exponentially, increased exponential annually and will be reach up to 6.3 exabytes per month by 2015. Demand for data traffic seems good and will be potential income for operators. But in fact revenue growth not directly proportional with traffic growth.
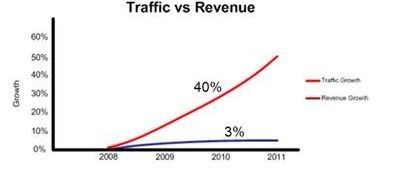
Why it could happened ? Indonesia is the largest youth mobile market in the region. Price wars between mobile operators that has began in 2007, along with handset saturation has driven mobile ARPU down. It could be impact for the mobile operators business in the future.
One of the telco management focuses in today's business climate is to scrutinize cost effectiveness for profit building opportunities. With this current business model, the only way to enhance better opportunities is by managing operational costs more effectively with the use of management radar.
Today, Activity-Based-Costing (ABC) is one of the strategic approach and profitability management tools. This tool can provide them with information related to products, customers, channels, related network operational and even the areas of profitability. In the middle of the value chain, organizations, such as distributors and wholesalers, have either sold their way to profitability (through growth strategies) or saved their way to profitability (through lean distribution, productivity improvement and maximizing asset utilization). ABC is a suitable approach for either cost collecting data and activity based to manage supply chain processes in order to inform and manage their way to that profitability.
In those processes, the major costs of supply chain organization are far more driven by customer demands than by their sales volume. Operational costs such as ordering, transportation, warehousing, selling and handling costs are driven by many factors like order size, product characteristics, packaging size/model, inventory requirements, geography, distance, vehicle, people etc. Today, managements believe that the costs associated with activities related to the processes are the most challenging for the costing approach to customers rather than to think about costs as being either fixed or variable. Why must they throw out fixed/variable cost thinking in this decision making? The reason is because of customers/subscribers driven costs. From the accounting perspective for costs, the ABC model is very different from the fixed/variable cost scheme. The advantages of using this approach are:
a). Management can identifying activities in the business and the resource costs associated with them
b). Management will have strategic data by assigning activities to things such as customers, products or processes. E.g : activities in a supply chain from ordering products, receiving and making payments to the manufacturer, selling products, delivery to and collection from retailers.
In the ABC model, resources represent people, network/technology, equipment/infrastructure, working capital and costs that associated with them. Customers, products and processes consume the resources and, therefore, incur costs. The ABC system assigns costs to these things based on their rate of consuming activities and, therefore it will be able to identify all resources and associated costs that go into the particular activity. ABC system defines all related functions in the organization in terms of the processes and activities that consume the resources of people, network/technology, equipment/infrastruucture and working capital, and incur the costs associated with the resources they consumed. The costs identified in the process activities are totaled, they are assigned to the customers, products or processes based on unit of activity, also called the cost driver. Usually the cost driver is the output that activity produces. The ABC system does not identify or assign costs based on their perceived behavior (fixed/variable), but rather based on what activities cause them and who consumes those activities.
ABC also identify whether the processes perform certain activities or not, meet customer expectation or not, reduce the cost of poor quality or not. Then it is a matter of assigning costs to customers if we are engaged in customer profitability analysis, assigning costs to principals if we are engaged in product profitability analysis or assigning costs to processes if we are trying to reduce the less valued added costs out of our business process. ABC can be considered a strategic costing approach and profitability management system. ABC provides the focus and information needed to deliver the output. Nowadays, customer profitability analysis, product line profitability analysis and business process analysis or any combinations of these purposes are widely used as a sophisticated model to manage their way to profitability. By using such information, the management can correctly assign costs to customers and principals based on the activity units they consume. Costs to serve are assigned below the gross profit line to determine the contribution and direct profit by customer and product line. Costs to serve are assigned based on the resources consumed by a particular customer, channel, product line, network/infrastructure and principals.
ABC's application to the customer, channels and product line profitability may differ from the information system perspective. An example is the SAP/R3 in which the information related to the ABC provides the data needed to generate a profit-loss statement for each customer or product line. With the use of such information, it is easier for the marketing and sales people to compute the return on investment as well as the payback period of investment by customers, channels and/or product group. It takes the management to the bottom line of customer and product line profitability, a point previously impossible to reach with traditional financial accounting systems, the systems designed as external financial reporting.
The use of ABC information by the management is not to track the cost of operations, but rather to make strategic decisions. The decision can be related to pricing, unbundling VAS, eliminating the cost of poor quality, managing customers/channels profitability and redesigning non value added processes. If the approach toward making these decisions is still powered by a fixed/variable cost mindset, the management will be running with the dumb decision making rules that the business uses every day.
Now, ABC offers a new way of thinking, one that starts with customer needs and ends with the cost to serve those needs. Wise advice for supply chain organization is to adopt the ABC approach in strategic costing management as the right tool for decision-making and discard fixed/variable cost thinking.
Author : Iqbal Zulkarnain
ABC ? sounds like soy souce brand ;D
What is ABC ? Lets continue read…..
Today, Internet is a rapidly growing market for multimedia services delivered to mobile devices, so called mobile internet Mobile. Mobile internet growth explosive on recent year. Mobile data traffic going exponentially, increased exponential annually and will be reach up to 6.3 exabytes per month by 2015. Demand for data traffic seems good and will be potential income for operators. But in fact revenue growth not directly proportional with traffic growth.

Why it could happened ? Indonesia is the largest youth mobile market in the region. Price wars between mobile operators that has began in 2007, along with handset saturation has driven mobile ARPU down. It could be impact for the mobile operators business in the future.
One of the telco management focuses in today's business climate is to scrutinize cost effectiveness for profit building opportunities. With this current business model, the only way to enhance better opportunities is by managing operational costs more effectively with the use of management radar.
Today, Activity-Based-Costing (ABC) is one of the strategic approach and profitability management tools. This tool can provide them with information related to products, customers, channels, related network operational and even the areas of profitability. In the middle of the value chain, organizations, such as distributors and wholesalers, have either sold their way to profitability (through growth strategies) or saved their way to profitability (through lean distribution, productivity improvement and maximizing asset utilization). ABC is a suitable approach for either cost collecting data and activity based to manage supply chain processes in order to inform and manage their way to that profitability.
In those processes, the major costs of supply chain organization are far more driven by customer demands than by their sales volume. Operational costs such as ordering, transportation, warehousing, selling and handling costs are driven by many factors like order size, product characteristics, packaging size/model, inventory requirements, geography, distance, vehicle, people etc. Today, managements believe that the costs associated with activities related to the processes are the most challenging for the costing approach to customers rather than to think about costs as being either fixed or variable. Why must they throw out fixed/variable cost thinking in this decision making? The reason is because of customers/subscribers driven costs. From the accounting perspective for costs, the ABC model is very different from the fixed/variable cost scheme. The advantages of using this approach are:
a). Management can identifying activities in the business and the resource costs associated with them
b). Management will have strategic data by assigning activities to things such as customers, products or processes. E.g : activities in a supply chain from ordering products, receiving and making payments to the manufacturer, selling products, delivery to and collection from retailers.
In the ABC model, resources represent people, network/technology, equipment/infrastructure, working capital and costs that associated with them. Customers, products and processes consume the resources and, therefore, incur costs. The ABC system assigns costs to these things based on their rate of consuming activities and, therefore it will be able to identify all resources and associated costs that go into the particular activity. ABC system defines all related functions in the organization in terms of the processes and activities that consume the resources of people, network/technology, equipment/infrastruucture and working capital, and incur the costs associated with the resources they consumed. The costs identified in the process activities are totaled, they are assigned to the customers, products or processes based on unit of activity, also called the cost driver. Usually the cost driver is the output that activity produces. The ABC system does not identify or assign costs based on their perceived behavior (fixed/variable), but rather based on what activities cause them and who consumes those activities.
ABC also identify whether the processes perform certain activities or not, meet customer expectation or not, reduce the cost of poor quality or not. Then it is a matter of assigning costs to customers if we are engaged in customer profitability analysis, assigning costs to principals if we are engaged in product profitability analysis or assigning costs to processes if we are trying to reduce the less valued added costs out of our business process. ABC can be considered a strategic costing approach and profitability management system. ABC provides the focus and information needed to deliver the output. Nowadays, customer profitability analysis, product line profitability analysis and business process analysis or any combinations of these purposes are widely used as a sophisticated model to manage their way to profitability. By using such information, the management can correctly assign costs to customers and principals based on the activity units they consume. Costs to serve are assigned below the gross profit line to determine the contribution and direct profit by customer and product line. Costs to serve are assigned based on the resources consumed by a particular customer, channel, product line, network/infrastructure and principals.
ABC's application to the customer, channels and product line profitability may differ from the information system perspective. An example is the SAP/R3 in which the information related to the ABC provides the data needed to generate a profit-loss statement for each customer or product line. With the use of such information, it is easier for the marketing and sales people to compute the return on investment as well as the payback period of investment by customers, channels and/or product group. It takes the management to the bottom line of customer and product line profitability, a point previously impossible to reach with traditional financial accounting systems, the systems designed as external financial reporting.
The use of ABC information by the management is not to track the cost of operations, but rather to make strategic decisions. The decision can be related to pricing, unbundling VAS, eliminating the cost of poor quality, managing customers/channels profitability and redesigning non value added processes. If the approach toward making these decisions is still powered by a fixed/variable cost mindset, the management will be running with the dumb decision making rules that the business uses every day.
Now, ABC offers a new way of thinking, one that starts with customer needs and ends with the cost to serve those needs. Wise advice for supply chain organization is to adopt the ABC approach in strategic costing management as the right tool for decision-making and discard fixed/variable cost thinking.
Author : Iqbal Zulkarnain
